When a general journal is correctly formatted and successfully created, accountants can easily track spending and identify any miscalculations that may exist. The information contained in a general journal can be used to help compile financial statements like income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. It is thus the book of entry for originally recording such types of transactions for which the organization has no special journal. The general journal is part of the accounting bookkeeping system. We call this event a transaction and record it in a speciality journal or in the general journal.
General journal entries examples
In these cases, a single journal entry will still include total debits and credits that are equal. Then, enter the date, the accounts, and the amounts in the general journal. Following these steps ensures that entries are recorded accurately and efficiently. Similar to combination journals, special journals are useful in streamlining the bookkeeping process.
Just a Few More Details
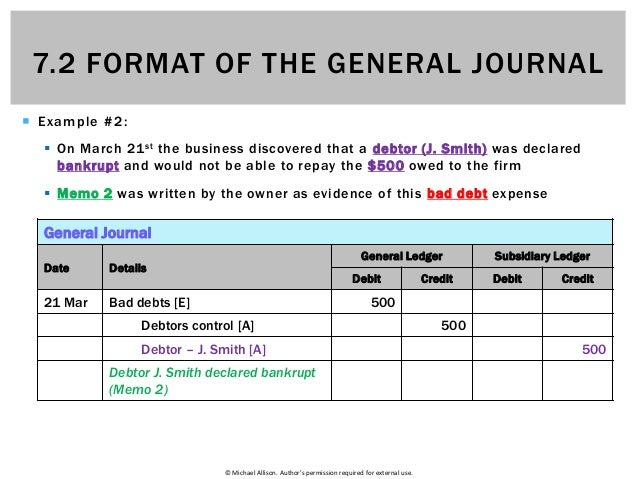
A brief description known as narration is also written in this column below the credit part of the entry. The year, month, and date of the transaction are written in the date column. It is written once per page (i.e., it does not have to be repeated for every entry on the page). There is an increase in an asset account (Furniture and Fixtures) in exchange for a decrease in another asset (Cash). It is used to record beginning balances, additions and deductions.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
- This is because all of this book initially records all of the business’s financial transactions before moving into other books.
- There are four journals specifically, which record transactions of a similar nature.
- It records each transaction chronologically, ensuring a comprehensive overview of all financial activities.
- As you can see in the general journal template above, the key information that should be included at the top is the name of the entity and the period that the journal is recording.
After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Other journals like the sales journal and cash disbursements journal are also used the help management organize and analyze accounting information. Throughout the accounting period, a business enters into transactions with customers, vendors, suppliers, the government, and other entities. All of these transactions must be recorded in order to accurately show the financial standings of the company at the end of the period. Having something this large typically isn’t practical, so most companies use the GL only to record general items like depreciation.
Journal Entry: Definition
All journal entries are posted periodically to the ledger accounts. Hence, the PR column is used to state what page the information was copied to when the financial transaction was recorded on the journal ledger; which has information about separate accounts. That is, the page number of the ledger account to which the entry belongs is written in the posting reference column. For instance, if the cash account is on page number 99 in the ledger, operating cash flow calculation the number 99 would be written in the posting reference column where the cash account appears in the general journal. In order to do this, a bookkeeper makes journal entries in the general journal recording changes in the corresponding accounts for a given transaction. For example, if a business purchased a new company vehicle for cash, the bookkeeper would record a journal entry that debits the vehicle account and credits the cash account.
Are General Journals the Same as General Ledgers?
There are four journals specifically, which record transactions of a similar nature. Their name suggests the kind of transactions that we record in them. These journals are Sales journal, Cash receipts journal, Purchases journal and Cash disbursements journal. For additional practice in preparing journal entries, here are some more examples of business transactions along with explanations on how their journal entries are prepared.
For example, under a double-entry bookkeeping system, you record a sales transaction in both the cash account and the sales revenue account simultaneously. However, in a single-entry bookkeeping system, you’ll only have to record the sales transaction in the cash account, without affecting another account. Examples of transactions recorded in the general journal are asset sales, depreciation, interest income and interest expense, and stock sales and repurchases. There are many special journals, and the four common types of special journals that normally use are Sales Journal, Purchase Journal, Cash Receipts Journal, and Cash Payments Journal. To complete an entry in a general journal, one would write a journal entry as usual.
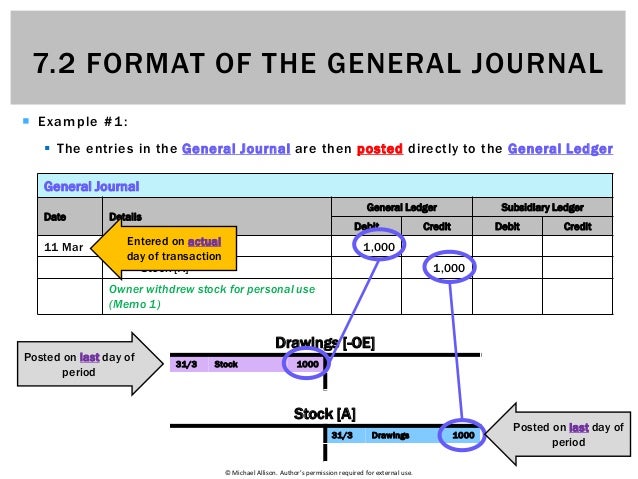
At least one line should be left blank before the next journal entry, and entries should not be split over more than one page. It has become a widespread practice to enter the debits first, followed by the credits and then the narration, though this is not a requirement. Nevertheless, whatever format you’ve adopted for your general ledger should be applied consistently. There are some accounting debit and credit rules to have in mind when using a general journal. In the general journal, there may be multiple debits or credit entries.
These entries typically include the date, accounts affected, and amounts. Understanding the structure and purpose of these entries is crucial for accountants and business owners alike. There are three types of accounting journal – general journal, combination journal and special journal.

